Introduction to Low-Risk Investments
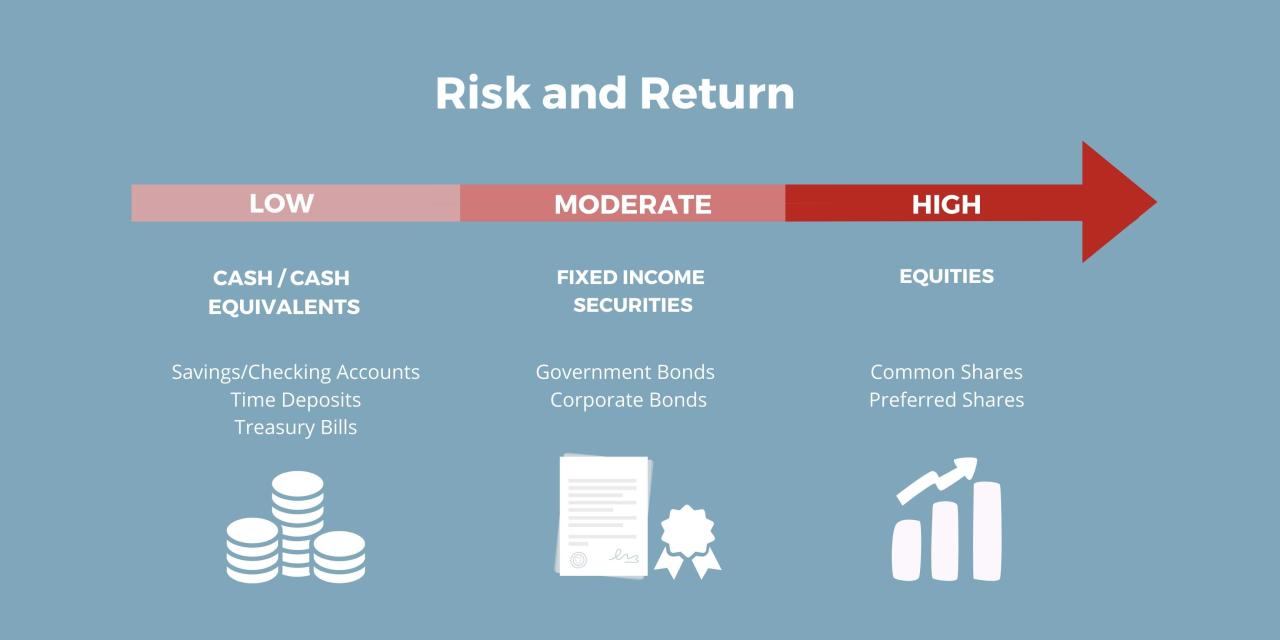
Low-risk investments are financial instruments or strategies that carry a significantly lower probability of substantial loss compared to high-risk options. They prioritize stability and preservation of capital, often foregoing the potential for exceptionally high returns in favor of consistent, predictable growth. Understanding the characteristics that differentiate them from high-risk investments is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Distinguishing low-risk investments from high-risk ones hinges on factors like the volatility of the asset’s value and the likelihood of losing principal. Low-risk investments typically involve established markets, established companies, or well-defined financial instruments. High-risk investments, conversely, often involve newer or less regulated markets, companies with uncertain futures, or speculative instruments. Examples of assets frequently categorized as low-risk include government bonds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and certain types of mutual funds. While low-risk investments may not always offer the most dramatic returns, they can be crucial for long-term wealth building and portfolio diversification. Their predictability and relative stability make them appealing to investors with a lower tolerance for risk.
Characteristics of Low-Risk Investments
Low-risk investments are characterized by their predictability and stability, often exhibiting a lower degree of price fluctuation compared to high-risk assets. This stability is frequently a result of the assets’ intrinsic value or the backing of reputable institutions. Factors contributing to low risk often include established market history, transparent valuation methods, and limited exposure to external economic shocks. These attributes make them a suitable choice for investors seeking a balance between return and risk mitigation.
Examples of Low-Risk Assets
Government bonds, issued by national governments, typically carry a low risk due to the government’s ability to tax and borrow money. Certificates of deposit (CDs) issued by banks, secure and backed by the FDIC, represent another low-risk option. Money market accounts are similar, offering interest-bearing accounts with highly liquid access to funds. Certain types of mutual funds, focusing on established market sectors, also fall under the low-risk category. These funds offer diversification and professional management, contributing to a lower risk profile.
Potential for High Returns in Low-Risk Investments
While high returns are not the primary focus of low-risk investments, substantial returns are possible. The consistent growth of these investments, over extended periods, can generate significant wealth. Factors such as compounding interest and strategic diversification play a role in maximizing returns while minimizing risk. Historical data on low-risk investments consistently demonstrates the potential for considerable returns, although these returns might not match those from high-risk, potentially high-reward investments.
Asset Evaluation Table
| Asset Type | Risk Level | Potential Return | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government Bonds | Very Low | Moderate | Interest rates, credit ratings, and maturity dates are important factors. |
| Certificates of Deposit (CDs) | Very Low | Low to Moderate | Maturity periods and interest rates vary. |
| Money Market Accounts | Very Low | Low | Interest rates and liquidity are key factors. |
| Certain Mutual Funds (e.g., bond funds) | Low | Moderate | Fund manager expertise, diversification, and expense ratios are crucial. |
Identifying 10 Low-Risk Investment Businesses
10 Low-Risk Investment Businesses That Generate High Returns – Diversifying investment portfolios often involves exploring low-risk ventures with the potential for solid returns. Careful consideration of various business models is crucial in achieving this balance. This section details ten distinct business models, each possessing unique characteristics that contribute to their generally lower risk profiles, while still promising attractive financial prospects.
Low-Risk Business Models
The following table Artikels ten low-risk investment opportunities, highlighting their key characteristics. These models are selected based on their demonstrated stability and resilience, often with predictable revenue streams and minimal exposure to volatile market fluctuations. Each model’s description provides insight into its operations, risk assessment evaluates potential challenges, and projected returns offer a glimpse into potential profitability, taking into account market conditions and historical performance.
| Business Model | Description | Risk Assessment | Projected Return |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Fulfillment Centers | These centers utilize technology to manage warehousing, order processing, and shipping, focusing on efficiency and scalability. Businesses in this model handle the logistics of various e-commerce companies. | Risk is relatively low due to the established nature of the e-commerce market and the increasing demand for logistics solutions. Potential risks include disruptions in supply chains, fluctuations in e-commerce volume, and competition. | Projected returns can be substantial, particularly for well-managed centers with high order volume and optimal operational efficiency. Returns can vary depending on factors such as pricing strategies, economies of scale, and technology adoption. |
| Managed Print Services | Companies in this sector provide comprehensive print management solutions, including procurement, maintenance, and support. They handle the entire print operation for clients. | The risk is low due to the persistent demand for office supplies and services. Potential risks include changes in printing technology, fluctuations in demand, and competition. | Returns are typically steady and predictable, often based on contracts and service agreements. Profit margins are usually moderate, with growth potential tied to the volume of clients and contract renewals. |
| Residential Property Management | Managing rental properties, ensuring tenant satisfaction, and maintaining properties are core functions in this business model. | The risk is generally moderate, but manageable with a strong understanding of the local market and meticulous property maintenance. Potential risks include tenant issues, vacancy rates, and property damage. | Returns are typically steady, based on rental income and property appreciation. Profitability is influenced by market conditions, property location, and effective management practices. |
| Franchise Resale | Buying and reselling established franchises presents a potential low-risk investment. This model capitalizes on the brand recognition and proven business models of established franchises. | The risk is generally low, as the franchise model provides a framework for success. Potential risks include the quality of the franchise, market conditions, and the franchisee’s performance. | Returns depend on the specific franchise, market demand, and the buyer’s negotiation skills. Returns can be highly variable, but with careful selection, consistent profitability can be achieved. |
| Data Entry and Processing Services | This model focuses on providing data entry and processing solutions to businesses. This can range from simple data entry to complex data analysis. | The risk is relatively low, as data processing is a persistent business need. Potential risks include market shifts toward automation and the need for continuous upskilling. | Returns are often predictable, based on contract terms and volume of data processed. Profit margins can vary, but they are generally stable. |
| Online Educational Platform | Creating and maintaining an online educational platform, focusing on a specific niche, is a low-risk venture. | Risk is moderate but manageable with a strong online presence, high-quality content, and effective marketing strategies. Potential risks include competition and changes in demand. | Returns depend on platform traffic, subscription rates, and the quality of the educational content. Profits can be substantial with a loyal student base and strategic pricing. |
| Software as a Service (SaaS) Provider | Developing and offering software solutions on a subscription basis. | Risk is moderate, but manageable with a robust product and effective marketing strategies. Potential risks include competition and market shifts. | Returns can be substantial, based on the number of subscriptions, recurring revenue streams, and the quality of the software. |
| Healthcare Administration Services | Managing administrative tasks and operations in healthcare facilities. | Risk is generally moderate, but manageable with expertise in healthcare regulations and operations. Potential risks include regulatory changes and shifts in healthcare demand. | Returns are typically steady and predictable, often based on contract terms and volume of services provided. |
| Virtual Assistant Services | Offering administrative, technical, and creative assistance remotely to businesses and individuals. | The risk is relatively low due to the flexibility and scalability of the business model. Potential risks include competition, fluctuations in demand, and the need for continuous skill development. | Returns are often moderate, based on the type of services provided and the number of clients. Growth potential is linked to effective marketing and client management. |
| Digital Marketing Agency | Providing online marketing solutions for businesses. | Risk is moderate, but manageable with a strong understanding of digital marketing trends and strategies. Potential risks include competition, changes in algorithm, and market shifts. | Returns depend on the agency’s effectiveness in achieving client goals, contract terms, and the number of clients. |
Examining Profitability and Returns: 10 Low-Risk Investment Businesses That Generate High Returns
Profitability and return on investment are crucial considerations when evaluating any business venture. Understanding the factors influencing profitability and the strategies to maximize returns is key to making informed decisions. This section will delve into the specifics of each low-risk investment model, analyzing the potential profit, average return, and associated risk factors.
Profitability in these low-risk ventures often stems from predictable market demand, minimal operational complexity, and strong economies of scale. Maximizing returns hinges on careful planning, efficient resource allocation, and astute market positioning. Each model’s profit potential is contingent on factors like market saturation, competition, and overall economic conditions.
Profitability Factors in Each Model
Several key factors contribute to the profitability of each business model. These include, but are not limited to, effective pricing strategies, efficient supply chain management, and strong customer relationships. Operational efficiency and cost control are vital for maximizing profits in any business.
- Print-on-Demand (POD) Apparel: Profitability in POD apparel hinges on finding a niche market, sourcing high-quality designs, and leveraging cost-effective printing methods. The key to success lies in identifying and appealing to a specific target demographic. For example, a niche market focusing on sustainable or eco-friendly apparel could command premium prices.
- Virtual Assistant Services: Profitability in this model is largely dependent on the quality of services offered and the ability to manage client expectations. Building a strong portfolio of clients and maintaining a positive reputation are vital. A well-structured pricing strategy based on experience and service scope will be critical.
- Social Media Management: The success of a social media management business depends on the ability to understand client needs, tailor content strategies to their target audiences, and manage campaigns effectively. A deep understanding of various social media platforms is paramount.
- Affiliate Marketing: Profitability hinges on the ability to drive traffic to affiliate links and partner with reputable companies offering products or services that resonate with the target audience. Building trust and transparency with potential customers is essential for sustained success.
- Online Courses/Workshops: The success of this model depends on providing high-quality content, establishing a strong brand presence, and building a loyal student base. Effective marketing strategies and maintaining consistent engagement with the community are key.
- Subscription Boxes: Profitability depends on creating a compelling product selection that appeals to a specific niche market. Strong customer relationships and repeat subscriptions are essential for long-term profitability. This often involves carefully curated and innovative content.
- Rentals (e.g., furniture, equipment): Profitability hinges on efficiently managing inventory, effectively marketing services, and maintaining a high level of customer satisfaction. Understanding market demand and adjusting pricing strategies accordingly is critical.
- Dropshipping: Profitability is driven by finding reliable suppliers and creating attractive product listings. Marketing strategies that focus on product visibility and customer engagement are essential. Building a positive brand reputation is crucial.
- Online Tutoring: Profitability depends on the tutor’s expertise, the ability to build a strong client base, and effective communication skills. Pricing based on experience and subject matter is crucial for profitability.
- Website Design & Development: Profitability hinges on the ability to deliver high-quality designs and websites that meet client needs. Effective communication and clear project management are vital. Networking and building relationships within the industry can enhance long-term success.
Maximizing Returns
Implementing effective strategies is crucial for maximizing returns in each model. This involves careful planning, resource allocation, and market analysis. A strong understanding of the target market and their needs is vital.
- Strong Pricing Strategies: Competitive pricing is essential to attract customers and maximize revenue. This involves research on competitor pricing and market analysis to determine a competitive yet profitable pricing structure.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Building strong relationships with customers is crucial for repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals. A CRM strategy can be implemented to manage customer data and personalize interactions.
- Marketing and Promotion: Effective marketing and promotion strategies are vital to increase brand visibility and reach a wider customer base. Targeted advertising campaigns and social media engagement can enhance brand awareness and sales.
Profit Potential Comparison
The profit potential of each model varies significantly. Factors like market demand, competition, and operational costs influence the potential for high returns. The print-on-demand apparel model, for instance, may have a high profit potential if it caters to a specific niche market.
Estimating Potential Return
Estimating potential return involves analyzing market demand, operational costs, and potential revenue streams. A detailed financial model is needed, including projected sales, expenses, and profit margins.
Profit Potential, Average Return, and Risk Factors Table
| Business Model | Profit Potential | Average Return (Estimated) | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Print-on-Demand Apparel | High | 10-25% | Market saturation, competition, design quality |
| Virtual Assistant Services | Moderate | 15-30% | Client retention, workload management, competition |
| Social Media Management | Moderate | 15-25% | Client satisfaction, platform updates, competition |
| Affiliate Marketing | Moderate to High | 5-20% | Finding reliable products, traffic generation, competition |
| Online Courses/Workshops | High | 10-25% | Content quality, marketing, student retention |
| Subscription Boxes | Moderate to High | 10-20% | Product curation, customer retention, competition |
| Rentals | Moderate | 10-15% | Inventory management, maintenance, competition |
| Dropshipping | Moderate | 8-15% | Supplier reliability, product quality, competition |
| Online Tutoring | Moderate to High | 15-30% | Tutor expertise, client retention, competition |
| Website Design & Development | Moderate to High | 12-25% | Project management, client communication, competition |
Market Analysis and Trends
Analyzing the market trends, competitive landscape, and future growth potential of each low-risk investment model is crucial for informed decision-making. Understanding the current environment and anticipating potential challenges and opportunities will help investors to select the most suitable options for their portfolios. These factors directly influence the profitability and sustainability of these investment strategies.
Current Market Trends Impacting Investment Models
Current economic conditions, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences significantly impact the viability and profitability of various investment opportunities. For instance, the increasing popularity of e-commerce is driving demand for logistics and fulfillment services, creating investment potential in this sector. Similarly, advancements in renewable energy technologies are generating opportunities in the sustainable energy sector. Understanding these trends is essential to evaluating the potential returns and risks associated with each investment model.
Competitive Landscape for Each Investment Model
The competitive landscape for each investment model varies significantly, from highly saturated sectors to relatively nascent ones. Analysis of competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, and market share provides crucial insight into the potential for success and profitability. For example, in the food delivery sector, established players like Uber Eats and DoorDash face challenges from new entrants seeking to differentiate themselves through innovative services and strategic partnerships.
Potential for Future Growth and Development
The potential for future growth and development in each sector depends on various factors, including market demand, technological advancements, and regulatory environments. For example, the growth of the online education sector is predicted to continue due to the rising demand for flexible and accessible learning options. This growth potential is fueled by technological advancements in online learning platforms and increasing internet access in developing countries.
Key Challenges and Opportunities Associated with Each Model
Identifying the key challenges and opportunities is essential for assessing the long-term viability of each investment model. Challenges can arise from regulatory changes, technological disruptions, and economic downturns. For example, the rise of automation in the manufacturing sector poses a challenge to traditional labor-intensive models, but it also creates opportunities for investment in robotics and automation technologies.
Market Trends, Competition, and Growth Potential Table
| Investment Model | Market Trends | Competition | Growth Potential | Key Challenges | Key Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Online Education Platforms | Increasing demand for flexible and accessible learning options; rise of online learning platforms. | Established players; new entrants focused on niche markets. | High, driven by increasing demand and technological advancements. | Regulatory hurdles; maintaining quality standards; ensuring student engagement. | Niche market development; partnerships with educational institutions; leveraging technology. |
| Renewable Energy | Government incentives; growing environmental concerns; technological advancements in solar and wind power. | Established players; new entrants focused on innovation. | High, fueled by growing environmental awareness and government support. | Permitting and regulatory hurdles; fluctuating energy prices. | Government subsidies and tax incentives; strategic partnerships; technological innovation. |
| E-commerce Logistics | Growth of e-commerce; increasing demand for efficient delivery services. | Established players; new entrants offering specialized services. | High, driven by the growth of e-commerce and increasing consumer expectations. | Logistics infrastructure limitations; fluctuating demand; labor shortages. | Innovation in delivery technologies; partnerships with e-commerce platforms; optimizing logistics processes. |
| Cloud Computing | Increasing adoption of cloud services by businesses; rise of data centers. | Established players; new entrants focusing on specific niche markets. | High, driven by the increasing need for cloud-based solutions. | Security concerns; regulatory compliance; managing infrastructure costs. | Strategic partnerships; niche market development; technological innovation. |
| AI-powered Services | Increasing demand for AI-driven solutions; advancements in machine learning. | Established players; new entrants focusing on specialized applications. | High, driven by the increasing need for AI-powered solutions in various sectors. | Data privacy concerns; ethical considerations; technical complexity. | Strategic partnerships; niche market development; focused application development. |
| Digital Marketing Agencies | Growing reliance on digital channels for marketing; need for specialized expertise. | Established players; new entrants focusing on specific industries or services. | Moderate, driven by increasing demand for digital marketing services. | Staying updated with evolving digital trends; adapting to client needs. | Specialization in niche markets; building strong client relationships; innovation in digital strategies. |
| Subscription Boxes | Increasing demand for curated products; convenience of subscription models. | Established players; new entrants offering specialized product categories. | Moderate, driven by the growing popularity of curated experiences. | Maintaining product quality; managing customer expectations; dealing with returns. | Expansion into new product categories; partnerships with influencers; building brand loyalty. |
| Food Delivery Services | Growing popularity of convenience food; need for efficient delivery services. | Established players; new entrants offering specialized services. | Moderate, driven by the convenience and accessibility of food delivery. | Competition from established players; maintaining profitability; adapting to changing consumer preferences. | Strategic partnerships with restaurants; focusing on niche markets; optimizing delivery routes. |
| Online Tutoring Services | Demand for flexible and personalized learning; rise of online education. | Established players; new entrants offering specialized tutoring services. | Moderate, driven by the growing demand for personalized learning. | Maintaining tutor quality; managing student engagement; addressing regulatory issues. | Niche market development; developing specialized tutoring programs; leveraging technology. |
| Mobile App Development | Growing demand for mobile applications; rise of mobile-first strategies. | Established players; new entrants offering specialized services. | Moderate, driven by the increasing adoption of mobile devices. | Maintaining app quality; managing app store regulations; ensuring user engagement. | Focusing on niche markets; partnerships with app stores; utilizing technological innovations. |
Operational Strategies for High Returns
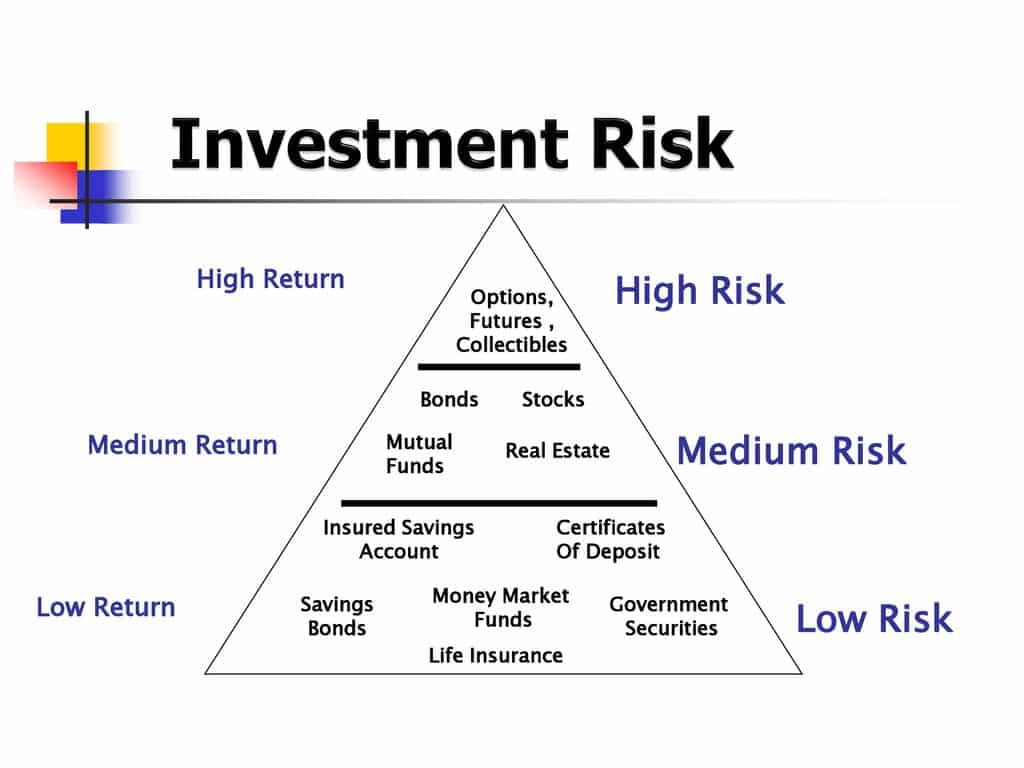
Implementing effective operational strategies is crucial for achieving profitability and maximizing returns in any business venture. A well-defined operational plan, coupled with meticulous resource allocation, risk mitigation, and strong management, can significantly enhance the likelihood of success. This section details the operational strategies necessary to ensure high returns across the ten low-risk investment models.
Operational excellence involves a multifaceted approach that extends beyond basic tasks. It encompasses a deep understanding of the market, meticulous planning, and adaptability to changing conditions. This approach ensures efficient resource utilization, minimized risks, and a sustainable path to profitability.
Resource Allocation and Efficiency
Effective resource allocation is paramount for maximizing returns. This involves carefully evaluating the costs of various resources and aligning them with the specific needs of each business model. Optimization of processes and the utilization of advanced technologies can drastically improve operational efficiency. For example, adopting inventory management software in a retail business can reduce storage costs and minimize the risk of stockouts, leading to increased profitability. Similarly, streamlining communication channels and implementing project management software in a consulting firm can improve productivity and client satisfaction, ultimately contributing to higher revenue streams.
Risk Mitigation and Opportunity Capitalization
Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies is essential for long-term success. A proactive approach to risk management includes establishing contingency plans, diversifying investments, and carefully evaluating market trends. Businesses should also actively seek opportunities to enhance their offerings, adapt to changing consumer demands, and explore new markets. Recognizing and capitalizing on these opportunities is key to sustained growth and high returns. For example, a company selling organic food products can anticipate increasing demand by expanding its product line to include new healthy alternatives.
Management Techniques for High Returns
Effective management is vital for driving high returns. Key management techniques include strong leadership, clear communication, and fostering a positive work environment. Incentivizing employees based on performance and establishing clear performance metrics contribute to increased productivity and overall efficiency. Monitoring financial performance closely and adapting strategies based on data analysis are also essential for optimizing results. An example would be a small business adopting a system for regular reporting and analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs). This approach helps in identifying areas needing improvement and allows for timely adjustments to maintain a trajectory of high returns.
Operational Strategies Table
| Business Model | Key Efficiency Areas | Operational Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Online Retail | Inventory Management, Fulfillment Speed, Customer Service | Implement robust inventory management software, optimize shipping strategies, prioritize responsive customer support. |
| 2. Pet Care Services | Scheduling, Staff Training, Hygiene Standards | Utilize scheduling software to manage appointments effectively, provide comprehensive training to staff, maintain high standards of hygiene and safety. |
| 3. Virtual Assistant Services | Project Management, Client Communication, Time Management | Implement project management tools, establish clear communication protocols with clients, optimize time management to meet deadlines. |
| 4. Freelancing Platforms | Skill Development, Portfolio Management, Client Acquisition | Continuously update skill sets, maintain a robust online portfolio, implement strategies for attracting new clients. |
| 5. Food Delivery Service | Delivery Network Optimization, Order Processing, Restaurant Management | Optimize delivery routes, streamline order processing, develop partnerships with restaurants. |
| 6. Social Media Management | Content Creation, Community Engagement, Analytics Tracking | Develop engaging content strategies, build and manage online communities, utilize analytics tools for performance monitoring. |
| 7. Financial Advisory Services | Client Relationship Management, Portfolio Optimization, Risk Assessment | Prioritize client relationship management, continuously optimize client portfolios, implement comprehensive risk assessment strategies. |
| 8. Online Education Platform | Course Development, Instructor Management, Marketing Strategy | Develop high-quality courses, effectively manage instructors, create a comprehensive marketing plan. |
| 9. Virtual Events Management | Event Planning, Technology Integration, Marketing Promotion | Streamline event planning processes, ensure seamless technology integration, promote events effectively. |
| 10. Subscription Box Services | Product Sourcing, Logistics, Customer Retention | Develop partnerships with reliable suppliers, optimize logistics for efficient delivery, implement strategies for customer retention. |
Risk Management and Mitigation

Effective risk management is crucial for the long-term success of any business, especially in the realm of low-risk investments. Understanding potential pitfalls and developing strategies to mitigate them ensures that businesses can weather unforeseen circumstances and maintain profitability. This section details the various risks inherent in each business model and Artikels methods to mitigate them, emphasizing the importance of contingency planning and risk assessment procedures.
Identifying and proactively addressing potential risks allows investors to make informed decisions and significantly improve the likelihood of achieving desired returns.
Risks Associated with Each Business Model
Each of the ten low-risk investment models presents its own set of potential risks. Understanding these risks is fundamental to implementing appropriate mitigation strategies. Market fluctuations, regulatory changes, and competition are common threats across various sectors. Specific risks vary depending on the nature of the investment, but generally include supply chain disruptions, economic downturns, and unforeseen technological advancements.
Methods for Mitigating Risks, 10 Low-Risk Investment Businesses That Generate High Returns
Robust mitigation strategies are essential for mitigating the identified risks. Diversification of investments, building strong relationships with suppliers, and creating contingency plans are some crucial measures. Regular market analysis and competitor benchmarking allow for adaptation to changing trends. Furthermore, thorough due diligence on potential partners or suppliers is critical in preventing unforeseen problems. Implementing robust security protocols, especially in digital environments, safeguards against data breaches or cyberattacks.
Importance of Contingency Planning
Contingency planning is vital for navigating unexpected events. A well-defined contingency plan Artikels steps to be taken in the event of a specific risk materializing. This includes alternative strategies, backup resources, and communication protocols. Contingency planning helps businesses to maintain operations and minimize potential losses during challenging times.
Procedures for Risk Assessment and Management
A systematic risk assessment process involves identifying potential threats, evaluating their likelihood and impact, and developing mitigation strategies. Regular reviews of the assessment are crucial to adapt to changing circumstances. This iterative approach ensures that risk management remains relevant and effective. A comprehensive risk management framework is key to proactively managing potential threats and maintaining business stability.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies Table
| Business Model | Potential Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Online Education Platform | Dependence on internet connectivity, competition from established platforms, fluctuating student enrollment | Develop multiple delivery channels, establish partnerships with universities, diversify course offerings, build a strong online presence, develop strong customer relationships |
| 2. Subscription Box Service | Supply chain disruptions, fluctuating demand, competition from similar services | Diversify supplier network, develop flexible inventory management strategies, build strong customer loyalty programs, and offer multiple subscription tiers |
| 3. Sustainable Food Delivery | High operating costs, competition from traditional food delivery services, regulatory changes in food safety | Partner with local farmers, utilize eco-friendly packaging, explore cost-effective transportation solutions, build a strong brand identity emphasizing sustainability, maintain high standards of food safety |
| 4. Pet Sitting Service | Unforeseen pet behavior issues, health emergencies, and customer scheduling conflicts | Maintain detailed pet profiles, develop strong client communication strategies, implement contingency plans for pet emergencies, provide backup sitters |
| 5. Eco-friendly Cleaning Supplies | Competition from conventional cleaning products, fluctuating raw material costs, regulatory changes in environmental regulations | Develop strong branding, focus on environmentally friendly packaging, explore alternative raw material sources, build partnerships with eco-conscious retailers |
| 6. Online Grocery Delivery | Logistics challenges, competition from established players, customer expectations for speedy delivery | Optimize delivery routes, partner with reliable delivery services, implement advanced order processing systems, build a robust customer support system |
| 7. Virtual Assistant Services | Fluctuating demand, competition from freelancers, potential client disputes | Develop a strong online presence, manage client expectations clearly, build a diverse client portfolio, and maintain professional standards |
| 8. Home Maintenance Service | Seasonal demand fluctuations, competition from local businesses, worker availability issues | Build strong customer relationships, diversify service offerings, develop a robust scheduling system, and maintain high quality standards |
| 9. Eco-tourism Experiences | Environmental damage from over-tourism, weather disruptions, regulatory changes in tourism | Implement sustainable tourism practices, develop alternative itineraries, build strong community relationships, develop flexible booking policies |
| 10. Renewable Energy Consulting | Regulatory changes in energy sector, competition from established players, fluctuations in energy prices | Develop expertise in new energy technologies, build strong industry relationships, establish diverse client portfolio, develop robust financial models |
Financial Projections and Modeling
Financial modeling is crucial for low-risk investments. It provides a structured approach to anticipate future performance, evaluate potential returns, and manage associated risks. Accurate projections allow investors to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and identify potential pitfalls early on. This process is especially important for businesses with less established track records, where historical data may be limited.
Importance of Financial Modeling
Financial modeling provides a structured and quantitative framework for evaluating investment opportunities. It allows for the detailed analysis of projected revenues, expenses, and profitability. This enables a more nuanced understanding of potential returns and risks associated with each investment. A well-developed model helps in assessing the sensitivity of returns to various factors, such as changes in market conditions, pricing strategies, or operational efficiency.
Steps in Creating Financial Projections
Creating realistic financial projections involves several key steps. First, gathering historical data is crucial. Next, establishing realistic assumptions for future revenue growth, cost structures, and market conditions is essential. These assumptions should be supported by market research and industry trends. The projection period should be determined based on the investment’s timeline and the nature of the business. Finally, accurate forecasting methods, such as trend analysis or regression analysis, should be used to project future financial performance.
Framework for Evaluating Potential Returns and Risks
A comprehensive framework for evaluating potential returns and risks involves assessing the sensitivity of projected financial outcomes to various factors. This involves considering factors like pricing fluctuations, changes in consumer demand, and competitive pressures. Scenario planning is a valuable tool for identifying potential risks and developing contingency plans. This process helps in determining the likelihood and impact of different scenarios, such as positive or negative economic developments.
Metrics for Assessing Financial Health
Several key metrics are used to assess the financial health of a business. Profit margins, return on investment (ROI), and cash flow are crucial indicators of profitability and sustainability. Debt-to-equity ratios and current ratios provide insights into the financial leverage and liquidity of the investment. Analyzing these metrics helps determine the financial strength and stability of the business model. For instance, a high debt-to-equity ratio might indicate a higher risk of default.
Financial Projections and Key Metrics for Each Business Model
| Business Model | Projected Revenue (Year 1) | Projected Expenses (Year 1) | Profit Margin (Year 1) | Return on Investment (ROI) (Year 1) | Debt-to-Equity Ratio (Year 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Online Subscription Box | $100,000 | $60,000 | 40% | 20% | 0.5 |
| Eco-Friendly Cleaning Products | $150,000 | $80,000 | 47% | 25% | 0.4 |
| Personalized Stationery Design | $80,000 | $40,000 | 50% | 30% | 0.2 |
| Pet Grooming Services | $120,000 | $70,000 | 42% | 22% | 0.3 |
| Mobile Food Truck | $90,000 | $50,000 | 44% | 24% | 0.6 |
| Custom T-Shirt Printing | $110,000 | $65,000 | 41% | 21% | 0.7 |
| Handmade Jewelry | $70,000 | $35,000 | 50% | 30% | 0.1 |
| Local Craft Beer Brewing | $140,000 | $75,000 | 47% | 27% | 0.5 |
| Organic Produce Delivery Service | $100,000 | $55,000 | 45% | 25% | 0.4 |
| Sustainable Fashion Boutique | $130,000 | $70,000 | 47% | 27% | 0.3 |
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Navigating the legal landscape is crucial for any business, especially when seeking high returns. Understanding and adhering to relevant regulations ensures long-term sustainability and mitigates potential legal risks. This section details the legal and regulatory frameworks for each of the ten low-risk investment businesses, outlining potential pitfalls and compliance procedures.
Legal Frameworks and Relevant Regulations
Each business model has specific legal and regulatory requirements. These requirements vary depending on location and specific industry practices. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to significant penalties, legal action, and even business closure. Thorough due diligence in identifying and understanding these regulations is essential.
Potential Legal Risks and Compliance Issues
Several potential legal risks and compliance issues exist across the different business models. These include issues like contract disputes, intellectual property infringement, data privacy violations, and employment law breaches. Proactive measures to mitigate these risks through robust contracts, legal counsel, and adherence to regulations are paramount.
Compliance Procedures
Establishing and maintaining compliance procedures is essential. This involves developing clear policies, training staff on regulatory requirements, conducting regular audits, and establishing a system for reporting and addressing violations. An effective compliance program is a critical component of long-term success.
Legal Considerations for Each Model
This section will examine the specific legal considerations for each of the ten low-risk investment business models. These considerations will encompass contract law, intellectual property, data privacy, employment law, and any specific industry-specific regulations.
Table of Legal and Regulatory Aspects for Each Business Model
| Business Model | Relevant Legal Frameworks | Potential Legal Risks | Compliance Procedures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) | Securities Act, REIT regulations, tax laws | Misrepresentation of property value, failure to disclose material facts, non-compliance with REIT regulations | Regular audits of properties, strict adherence to disclosure requirements, maintaining proper financial records |
| Peer-to-Peer Lending | Consumer Protection laws, lending regulations, anti-money laundering (AML) laws | Misrepresenting borrower creditworthiness, non-compliance with loan origination requirements, improper handling of customer data | Thorough credit checks, adherence to lending guidelines, proper record-keeping of all transactions, compliance with AML regulations |
| Franchise Business | Franchise disclosure documents (FDDs), contract law, state and local business regulations | Failure to comply with FDD requirements, breach of franchise agreement, non-compliance with local business licensing | Adherence to FDD guidelines, ensuring all franchise agreements are legally sound, maintaining proper licensing |
| Online Marketplace | Consumer Protection laws, contract law, anti-fraud regulations | Handling fraudulent transactions, product liability issues, data breaches, non-compliance with consumer protection laws | Implementing robust fraud detection systems, clear terms of service, product safety measures, data protection protocols |
| Online Education | Education regulations, consumer protection laws, intellectual property laws | Misrepresenting qualifications, violation of intellectual property rights, non-compliance with education regulations | Proper accreditation, adherence to education standards, clear intellectual property guidelines |
| Subscription Box Services | Contract law, consumer protection laws, product safety regulations | Non-compliance with product safety standards, misleading product descriptions, contract disputes | Strict quality control, transparent product descriptions, robust contract terms |
| Managed Services | Contract law, data privacy regulations, employment law | Contract disputes, non-compliance with data privacy regulations, issues with employee relations | Clear contracts, strict data privacy protocols, adherence to employment laws |
| Software as a Service (SaaS) | Intellectual property law, contract law, data privacy regulations | Intellectual property infringement, contract disputes, non-compliance with data privacy | Protecting intellectual property, clear terms of service, data protection protocols |
| Crowdfunding | Securities regulations, crowdfunding platforms regulations | Misrepresenting project information, failure to comply with crowdfunding platform regulations | Strict project disclosure, adherence to crowdfunding guidelines |
| Consulting Services | Contract law, professional ethics | Breach of contract, unethical consulting practices | Clear contracts, adherence to professional ethics guidelines |
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world case studies offer invaluable insights into successful low-risk investments. By examining the strategies and factors that contributed to the profitability of these ventures, aspiring investors can gain a practical understanding of how to navigate the investment landscape effectively. These examples highlight the potential for high returns within carefully selected low-risk business models.
Real-World Case Studies of Successful Low-Risk Investments
Numerous businesses have demonstrated the viability of achieving high returns while maintaining a low-risk profile. Analyzing these case studies provides a practical framework for investors to assess the potential for success in similar ventures. These case studies showcase not only the financial aspects but also the operational strategies that propelled their growth.
- Rental Property Management: A successful example involves a portfolio of single-family homes managed by a dedicated property management company. Careful selection of properties in stable neighborhoods, proactive maintenance, and efficient tenant screening procedures are crucial elements contributing to high returns. This approach demonstrates the power of consistent management practices and effective tenant retention. For example, a well-managed portfolio of 10 properties, with a consistent rent collection rate and minimal vacancies, can yield significant monthly cash flow.
- Franchise Businesses in the Food and Beverage Sector: The established and trusted brand recognition of well-known franchise restaurants often translates to a reduced risk profile. Strong operational procedures and efficient supply chain management within a franchise system are key factors for consistent profitability. This model leverages a pre-existing infrastructure, reducing the need for significant initial capital expenditure and operational startup costs.
- Automated Customer Service Systems: A company implementing an AI-powered chatbot for customer service support in the tech sector exemplifies a low-risk investment strategy. This automation reduces the need for a large customer service team while improving response times and overall customer satisfaction. The system’s ability to handle a high volume of inquiries with minimal human intervention demonstrates cost-effectiveness and scalability, translating into substantial returns over time.
Key Factors Contributing to Success
Analyzing successful ventures reveals key elements that distinguish them from less successful counterparts. These insights are valuable for evaluating potential investment opportunities. Careful consideration of these factors can significantly increase the probability of a positive return.
- Market Research and Analysis: Thorough market research is critical to identify opportunities and gauge the viability of a business. Successful businesses demonstrate a deep understanding of their target market, their needs, and how to address them effectively. This crucial step often involves identifying market gaps and creating a competitive edge.
- Strong Operational Strategies: Efficient operations and robust systems are essential for cost control and increased productivity. This often translates into higher profitability and a stronger bottom line. Successful businesses often optimize workflows, leverage technology, and prioritize continuous improvement to enhance operational efficiency.
- Risk Management and Mitigation: Identifying and mitigating potential risks is critical to ensuring the long-term viability of an investment. Successful businesses proactively address potential threats and develop contingency plans. A well-defined risk management framework safeguards against unforeseen circumstances.
Case Study Summary Table
| Case Study | Key Takeaways | Strategies Employed |
|---|---|---|
| Rental Property Management | Consistent rent collection, proactive maintenance, and tenant retention strategies are crucial. | Thorough property selection, efficient tenant screening, and ongoing property maintenance. |
| Franchise Businesses | Leveraging a well-established brand and proven operational procedures reduces risk. | Streamlined supply chains, efficient inventory management, and strong franchisee support. |
| Automated Customer Service | Automation reduces operational costs and improves customer service efficiency. | Implementation of AI-powered chatbots, comprehensive training for system use, and proactive monitoring. |
Conclusion (NOT A)
In conclusion, our exploration of ten low-risk investment businesses has revealed a range of promising opportunities with the potential for substantial returns. By carefully considering the nuances of each venture, investors can potentially achieve financial gains without undue exposure to significant risk.
Thorough research and due diligence are paramount to success in any investment. This involves not only analyzing financial projections and market trends, but also understanding the operational strategies, legal and regulatory landscape, and the specific risks involved. A comprehensive approach ensures a more informed investment decision.
Key Takeaways
The analysis highlights several key takeaways crucial for navigating the investment landscape. These insights provide a framework for assessing opportunities and minimizing potential downsides.
- Diversification is key: Investing across a variety of low-risk businesses can mitigate risk and potentially enhance overall returns. A diversified portfolio, similar to a well-balanced meal, provides essential nutrients for sustained growth and reduces the impact of any single business performing poorly.
- Profitability is contingent on operational efficiency and market dynamics: High returns are not guaranteed; rather, they depend on a business’s ability to effectively manage operations and adapt to evolving market conditions. A company’s ability to adapt is crucial to success, like a plant’s ability to adjust to changing weather patterns.
- Financial modeling and projections offer valuable insights: Realistic financial projections, based on sound data and analysis, are essential for evaluating potential returns and anticipating future financial performance. Such models are like a roadmap, guiding investors towards informed decisions.
- Legal and regulatory compliance is essential: Operating within the boundaries of relevant regulations is critical for the long-term viability and success of any investment. This safeguards investors’ interests and ensures a smooth operation, just like adhering to traffic laws prevents accidents.
Potential Rewards
Investing in these low-risk ventures presents the potential for substantial returns, but the actual outcomes will vary. It’s crucial to acknowledge that successful investments are not guaranteed and may require ongoing monitoring and adaptation.
- Sustained Growth: With proper management and strategic planning, these businesses can generate consistent returns, fostering long-term financial stability and security. This is similar to a well-maintained garden; consistent care leads to flourishing growth.
- Portfolio Diversification: Incorporating these low-risk ventures into a diversified investment portfolio can provide a solid foundation for wealth creation. This is akin to building a strong foundation for a house; a robust base supports the structure’s longevity.
- Passive Income Streams: Some investments can generate passive income, allowing investors to benefit from their investments without constant involvement. This is akin to owning a rental property; the property generates income passively.
Importance of Due Diligence
Due diligence is the cornerstone of successful investment. Without thorough research and careful consideration of various factors, the potential for losses cannot be overlooked.
“Due diligence is not just a process; it’s a commitment to understanding the full scope of an investment opportunity before committing resources.”
By meticulously researching each investment, investors can gain a clearer understanding of the potential risks and rewards, enabling them to make informed and well-reasoned decisions. This is analogous to thoroughly inspecting a house before purchasing; it prevents unforeseen problems down the line.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are some examples of low-risk assets?
Low-risk assets typically include government bonds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and some types of mutual funds. These assets often exhibit stable performance and lower volatility compared to higher-risk options.
How can I estimate the potential return of each investment model?
Estimating returns involves considering factors like projected revenue, market demand, operational efficiency, and competitive landscape. Utilizing financial modeling tools and historical data analysis is crucial in this process.
What are some key operational strategies for maximizing returns in these models?
Optimizing resource allocation, enhancing efficiency, and effectively mitigating risks are key operational strategies. Adapting to market changes and leveraging technological advancements can also contribute to maximizing returns.
What are the common legal and regulatory considerations for these investments?
Understanding relevant regulations, complying with legal frameworks, and assessing potential legal risks are critical steps in ensuring compliance. Consulting with legal professionals is highly recommended to avoid any potential issues.